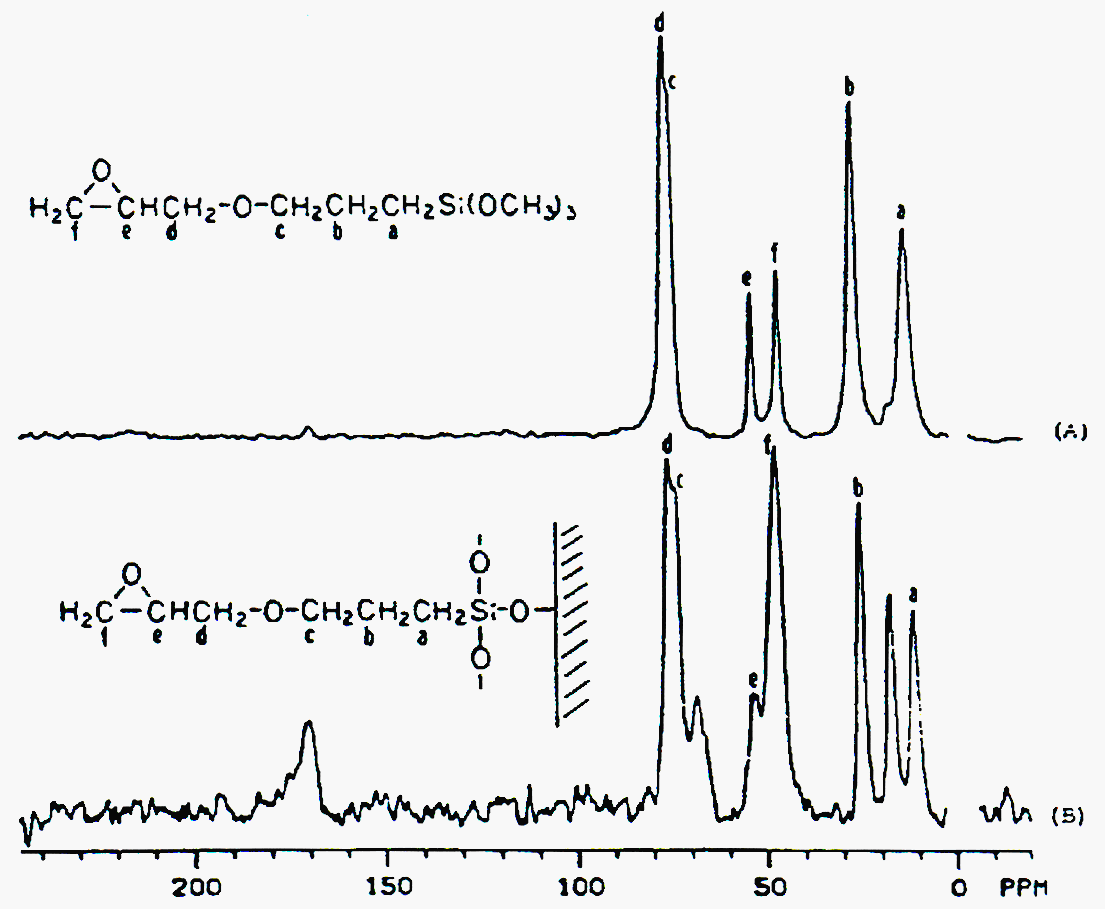
Pictured above is a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, NMR (macrogalleria). NMR is another method for analyzing polymer matrices and composite interphases. Materials, specifically polymers, have atoms which display certain chemical shifts upon excitement by NMR and are affected by the environment they are in. At the interphase, atoms find themselves in a totally different environment than that of the pure matrix material. As a result, in some cases, the interphase can be characterized by the chemical shifts of the materials involved in the interphase. A great deal of work has been done in the area of silica surfaces with NMR. Below is a relevant NMR spectra of gamma-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (gamma-GPS) both (A) polymerized and (B) on a silica surface such as glass. Notice the different resonance as the environment of the gamma-GPS is changed.