Polymerization of polyamides is the formation of the functional group,
amide, between a carboxylic acid or carboxylic acid derivative and amine.
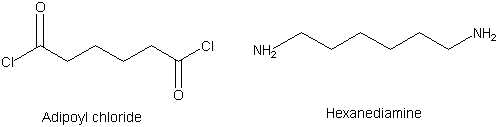
It usualy needs two functional groups of each reactants,
so we use adipoyl chloride and hexanediamine,
which have two acid chloride and amine groups in the reactants.
Formation of Amides

Formation of Amides
The carboxylic acids and its derivatives have a different reactivity from
the ketones and aldehydes, even though they have same carbonyl group.
They react with incoming nucleophile to give the carboxylic acid derivatives
in the reaction of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
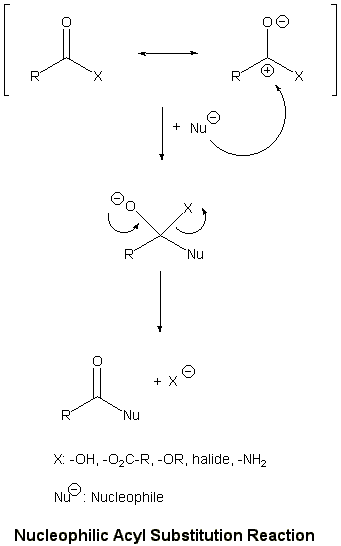
The amide functional group can be formed with acid or no catalyst.

Nylon 6,6 will be formed with acid, NH4Cl, diacid, adipoyl chloride, and diamine, Hexanediamine.