

Keywords:
amorphous,
crystal
We talk about glass from time to time when we're discussing polymers,
especially when we're talking about composite
materials. Glass fibers are often used to
reinforce polymers. But what is this stuff called glass? We use it with
polymers a lot, obviously, but is glass itself a polymer?
Before we tackle that question, let's take a look at what glass is. The highest quality glass has the chemical formula SiO2. But this is misleading. That formula conjures up ideas of little silicon dioxide molecules, analogous to carbon dioxide molecules. But little silicon dioxide molecules don't exist.

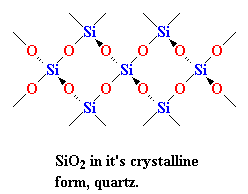 Instead, in nature SiO2 is often found as a crystalline solid, with a structure like you see on your right. Every silicon atom is bonded four oxygen atoms, tetrahedrally, of course; and every oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms. When SiO2 is in this crystalline form we call it silica. You've seen silica before. When you find big honkin' crystals of it we call it quartz. When we have a lot of little tiny crystals of it, we call it sand.
Instead, in nature SiO2 is often found as a crystalline solid, with a structure like you see on your right. Every silicon atom is bonded four oxygen atoms, tetrahedrally, of course; and every oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms. When SiO2 is in this crystalline form we call it silica. You've seen silica before. When you find big honkin' crystals of it we call it quartz. When we have a lot of little tiny crystals of it, we call it sand.
But this silica isn't glass. We have to do something to it first to make it into glass. We have to heat it up until it melts, and then cool it down really fast. When it melts, the silicon and oxygen atoms break out of their crystal structure. If we cooled it down slowly, the atoms would slowly line back up into their crystalline arrangement as they slowed down. (Remember, heat is really just the random motion of atoms and molecules. Hot atoms move a lot, cold atoms move very little.)
But if we cool it down fast enough, the atoms of the silica will be stopped in their tracks, so to speak. They won't have time to line up, and they'll be stuck in any old arrangement. They'll look something like this:

 As you can see, there is no order to the arrangement of the atoms. We call materials like this amorphous. This is the glass that is used for telescope lenses and such things. It has very good optical properties, but it's brittle. For everyday uses, we need something tougher. Most glass is made from sand, and when we melt down the sand, we usually add some sodium carbonate. This gives us a tougher glass with a structure that looks like this:
As you can see, there is no order to the arrangement of the atoms. We call materials like this amorphous. This is the glass that is used for telescope lenses and such things. It has very good optical properties, but it's brittle. For everyday uses, we need something tougher. Most glass is made from sand, and when we melt down the sand, we usually add some sodium carbonate. This gives us a tougher glass with a structure that looks like this:

So is this a polymer or not? Usually it isn't considered as such. Why? Some may say it's inorganic, and polymers are usually organic. But there are many inorganic polymers out there. For example, what about polysiloxanes? These linear, and yes, inorganic materials have a structure very similar to glass, and they're considered polymers. Take a look at a polysiloxane:

So glass could be considered a highly crosslinked polysiloxane. But we usually don't think of it that way. Why not? Probably because even in a highly crosslinked system, you could still trace a polymer chain and see where the crosslinks are. But with glass, it'd be tough to do that.
|
Return to Level Three Directory |

|
Return to Macrogalleria Directory |
