Keywords
ion
One example of an ionomer is poly(ethylene-co-methacrylic acid). This polymer is a sodium or zinc salt (which provides the ions) of copolymers derived from ethylene and methacrylic acid.

The ionic attractions that result strongly influence the polymer properties. Let's take a look at how ionomers work.
In an ionomer, the nonpolar chains are grouped together and the polar ionic groups are attracted to each other. The ionic groups would like to go off into a little corner by themselves, but since they are attached to the polymer chain, they cannot. This allows thermoplastic ionomers to act in ways similar to that of crosslinked polymers or block copolymers. Take a look.
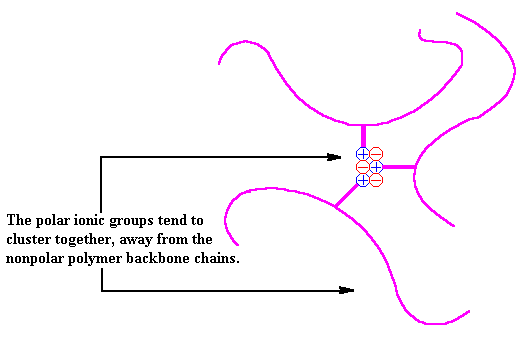
However, ionomers are not crosslinked polymers, and are in fact a type of thermoplastic called a reversible crosslinker. When heated, the ionic groups will lose their attractions for each other and the chains will move around freely. As the temperature increases, the chains move around faster and faster and the groups cannot stay in their clusters. This allows for a polymer with the properties of an elastomer and the processability of a thermoplastic. These ionomers are sometimes known as thermoplastic elastomers. Imagine that!

So far, we've only talked about what are called random ionomers. A random ionomer is one where the ionic groups are attached to the backbone chain at random intervals. However, there are a few other types of ionomers.
Another use for ionomers is that of a semi-permeable membrane. A semi-permeable membrane is a very thin piece of material lets some materials pass through while others remain inside. The membranes made with ionomers are called specifically ion-selective membranes. These ion-selective membranes work by letting water pass through and not the metal ions.
One specific ion-selective membrane is a perfluorosulfonate ionomer which DuPont calls Nafion. All perfluorosulfonate ionomers have outstanding chemical and thermal stability and the ability to absorb incredible amounts of water. Nafion membranes can be made into films or tubes and can be used in many caustic and dangerous processes. Some such processes are the production of chlorine, regeneration of spent acids, separations in chemical processing, as well as uses in fuel cells and electrodialysis.
|
Return to Level Three Directory |

|
Return to Macrogalleria Directory |