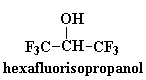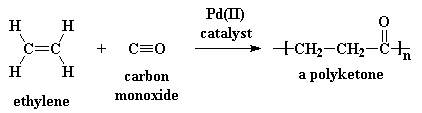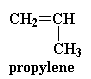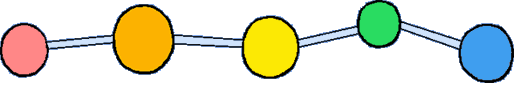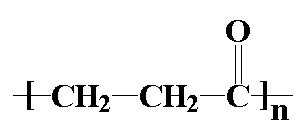

The model on the right above is an image of the pdb model you can view by clicking here or you can just click on the image itself.
Either way, be sure to close the new window that opens up with the 3D model in it when you are ready to come back here.
For polyketones at a glance, click here!
I would just love to tell you that many wonderful things are
made of polyketones, but I can't. You see, these polymers are so new that
not much has been made out of them yet. But polyketones, which are plastics, by the way, have a lot going
for them, and we figure it won't be long before a lot of stuff is made
from them.
 So what's so great about polyketones? Let's find out by taking a look at
them. A polyketone is of course a polymer with a ketone group in
the backbone chain. The polyketones we're going to talk about on this
page are based on the picture you see at the top of the page, where
R' is an ethylene linkage, -CH2CH2-. Shell
has just put this family of polymers on the market and sells them under
the name Carilon. This is not to be confused with a carillon,
which is a musical instrument with differently pitched bells, which
are often
controlled with a piano-like keyboard. Let's see what one of these polymers looks like, next to a chain of good
ol' polyethylene for comparison:
So what's so great about polyketones? Let's find out by taking a look at
them. A polyketone is of course a polymer with a ketone group in
the backbone chain. The polyketones we're going to talk about on this
page are based on the picture you see at the top of the page, where
R' is an ethylene linkage, -CH2CH2-. Shell
has just put this family of polymers on the market and sells them under
the name Carilon. This is not to be confused with a carillon,
which is a musical instrument with differently pitched bells, which
are often
controlled with a piano-like keyboard. Let's see what one of these polymers looks like, next to a chain of good
ol' polyethylene for comparison:
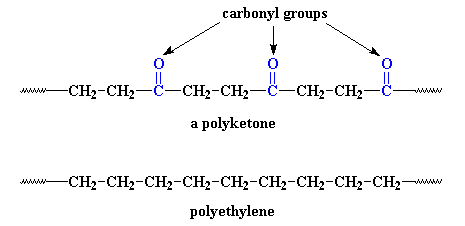
 It's not much different. The only difference is that the polyketone has
those carbonyl groups in it. But those carbonyls do a lot. You see,
carbonyl groups are very polar.
This is because oxygen is electronegative
and draws electrons away from the carbon atom. So oxygen has a slight
negative charge and the carbon has a slight positive charge.
These polar carbonyl groups are attracted to each other, and very strongly
at that. This attraction is so strong that while polyethylene melts at a
mere 140oC, the polyketone doesn't melt until 255 oC!
It's not much different. The only difference is that the polyketone has
those carbonyl groups in it. But those carbonyls do a lot. You see,
carbonyl groups are very polar.
This is because oxygen is electronegative
and draws electrons away from the carbon atom. So oxygen has a slight
negative charge and the carbon has a slight positive charge.
These polar carbonyl groups are attracted to each other, and very strongly
at that. This attraction is so strong that while polyethylene melts at a
mere 140oC, the polyketone doesn't melt until 255 oC!
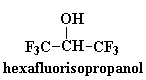
These polyketones have another interesting property. They won't dissolve
in much of anything. To dissolve it you have to use something really
weird like hexafluoroisopropanol. This comes in handy should you want to
make a car part out of this stuff. A car part is no good if it dissolves
when you spill gasoline on it. But that's no problem with polyketones!
This is all very nice, but really, now, what's the big deal? There are
lots of high performance plastics out there. There are poly(ether sulfones), poly(phenylene sulfide), polyimides... We've seen high performance
before. What makes polyketones so special?
This is what makes polyketones so special. To make polyketones, you take
ethylene gas and carbon monoxide, and react them with a palladium(II)
catalyst:
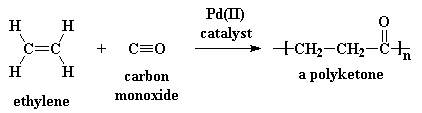
Ethylene is dirt cheap; it's the monomer for polyethylene. Carbon monoxide is dirt cheap, too.
You make carbon monoxide every time you burn wood, or a candle, or just
about anything containing carbon. The reaction is also easy to carry out.
Most high performance polymers are difficult to make, because the
chemistry has to be just right for the reactions to work.
Cheap monomers, and easy chemistry make polyketones rather cheap, a whole
lot cheaper than other high performance plastics.
In time the price may come down to less than a dollar per pound! This is why we think a lot of
stuff is going to be made out of
polyketones in the future.
Here's some models of the monomers if you want to play with them. Ethylene is on the left and carbon monoxide is on the right.

The models above are images of the pdb models you can view by clicking on each image itself.
Either way, be sure to close the new window that opens up with the 3D model in it when you are ready to come back here.
One Last Detail
There was a problem with this polyketone when Shell first made it. You
see, these polymers are very highly crystalline, that is,
the polymer chains are packed together in a very orderly fashion. This makes the polyketones
very strong, but the down side is that it also makes them very brittle. the
chemists went to work and came up with a solution. They decided to throw
a little bit of propylene in with the ethylene and the carbon monoxide
when they make the polymer.
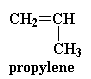
Propylene reacts just like ethylene does, so
we end up with a polymer that looks like this:

Every now and then you get an extra methyl group attached to one of the
ethylene units. These methyl groups get in the way when the polymer
chains try to pack into crystals. They can still pack, but not as well as
before. The bad part is that the melting temperature drops to about 220
oC, because the crystals aren't as strong. But the good part
is that the polymer is now a lot tougher and less brittle.
This polyketone made with ethylene, carbon monoxide, and a little bit of
propylene is the Carilon that you can buy.
Keep watching this page. As soon as we find out what people are making
out of these polyketones, we'll post something here about it!
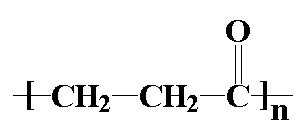


 So what's so great about polyketones? Let's find out by taking a look at
them. A polyketone is of course a polymer with a ketone group in
the backbone chain. The polyketones we're going to talk about on this
page are based on the picture you see at the top of the page, where
R' is an ethylene linkage, -CH2CH2-. Shell
has just put this family of polymers on the market and sells them under
the name Carilon. This is not to be confused with a carillon,
which is a musical instrument with differently pitched bells, which
are often
controlled with a piano-like keyboard. Let's see what one of these polymers looks like, next to a chain of good
ol'
So what's so great about polyketones? Let's find out by taking a look at
them. A polyketone is of course a polymer with a ketone group in
the backbone chain. The polyketones we're going to talk about on this
page are based on the picture you see at the top of the page, where
R' is an ethylene linkage, -CH2CH2-. Shell
has just put this family of polymers on the market and sells them under
the name Carilon. This is not to be confused with a carillon,
which is a musical instrument with differently pitched bells, which
are often
controlled with a piano-like keyboard. Let's see what one of these polymers looks like, next to a chain of good
ol' 
 It's not much different. The only difference is that the polyketone has
those carbonyl groups in it. But those carbonyls do a lot. You see,
carbonyl groups are very polar.
This is because oxygen is electronegative
and draws electrons away from the carbon atom. So oxygen has a slight
negative charge and the carbon has a slight positive charge.
These polar carbonyl groups are attracted to each other, and very strongly
at that. This attraction is so strong that while polyethylene melts at a
mere 140oC, the polyketone doesn't melt until 255 oC!
It's not much different. The only difference is that the polyketone has
those carbonyl groups in it. But those carbonyls do a lot. You see,
carbonyl groups are very polar.
This is because oxygen is electronegative
and draws electrons away from the carbon atom. So oxygen has a slight
negative charge and the carbon has a slight positive charge.
These polar carbonyl groups are attracted to each other, and very strongly
at that. This attraction is so strong that while polyethylene melts at a
mere 140oC, the polyketone doesn't melt until 255 oC!